Heat Treating: Equipment
Equipment
Combustion Technology
Energy Consumption
Process Description
R&D Trends

Courtesy of SECO/WARWICK
Heat treating encompasses a wide variety of processes by which carefully controlled changes in the temperature of the metal are used to improve the materials mechanical properties and stress conditions. Heat treating is not only used for creating the desired mechanical properties in the final products, but is also used in intermediate steps of the fabrication process. There are a variety of different types of ovens and furnaces used for heat treating aluminum.
Furnace Types:
Atmosphere Furnace (photo courtesy SECO/WARWICK)

Courtesy of SECO/WARWICK
To prevent high temperature surface oxidation of metal during heat treating, air tight furnaces are used which replace the air in the furnace with a process atmosphere which is low in oxygen and prevents oxidation of the product. There are two basic types of gas atmospheres most commonly used in heat treating processes:
Exothermic
Exothermic atmospheres are generated using a slightly rich combustion of natural gas. Atmospheres generated using air-to-gas ratios greater than 5:1 are termed exothermic.
Endothermic
Endothermic atmospheres are generated using a very rich combustion of natural gas and air. Air-to-gas ratios less than 5:1 are termed endothermic.
Box Furnace (photo courtesy Aichelin-Stahl)

Courtesy of Aichelin-Stahl
Box furnaces are similar in design to slot furnaces except that they have a door that can be closed. The majority of forging furnaces used in the United States are box furnaces. They are relatively simple, consisting of refractory lined walls, a door, a hearth for supporting the metal charge, and the burner system.
Car Bottom Furnace (photo courtesy Aichelin-Stahl)

Courtesy of Aichelin-Stahl
Car bottom furnaces have a movable bottom with the door attached to the bottom. The material is loaded on the movable car and then moved into position. This type of furnace is typically used for large forgings requiring a number of forging steps with reheats between forgings. Optional designs have pass-through car bottoms, or configurations which can accommodate more than one car.
An advantage of this type of furnace is that it provides easy access to load and unload the furnace bottom while it is outside the furnace.
Hearth Furnaces (photo courtesy Surface Combustion, Inc.)
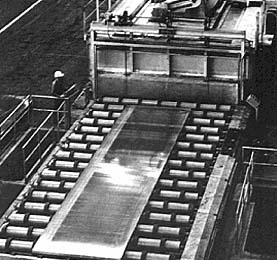
Courtesy of Surface Combustion, Inc.
Roller and conveyor hearth furnaces are continuous furnaces which transport the material through a horizontal furnace either on rollers or on a conveyor belt. Burners within the furnace heat the charge to the desired temperature and the speed of the conveyor or rollers determines the time spent in the furnace. These furnaces provide the benefit of continuous processing.
Induction Furnace Pusher Furnace (photo: “Induction System for heating bar stock prior to forging”, courtesy of Inductoheat, Inc.)

Induction system for heating bar stock prior to forging.
Courtesy of Inductoheat, Inc.
Electric induction furnaces use electromagnetic forces to heat the aluminum stock. A typical induction furnace used for heating aluminum billets prior to hot working uses a combination of electromagnetic and gravitational forces to move through a steady line of billets through the induction coil. Billets emerging at the exit of the coil are removed from the line.
In well suited applications, induction furnaces are very efficient, fast, and cut down on surface oxidation. It can be difficult though, to fine tune the furnace to the optimum heating frequency, and capital and operating costs are high.
Pusher Furnace (“Preheating aluminum billets in support of extrusion or other hot forming operations”, courtesy of Despatch Industries. )

Preheating of aluminum billets in support of extrusion or other hot forming operations.
Courtesy of Despatch Industries
Pusher furnaces are, in effect, an open tube with burners surrounding the stock. The material is pushed through on a line end to end. In counterflow pusher furnaces there are two zones. In the first zone, the stock is heated by exhaust gases from the second zone which heats the stock to the desired temperature. Most pusher furnaces currently in operation use radiant burners to reduce hot spots and maintain temperature uniformity, but low thermal efficiency has prompted the industry to adopt higher efficiency direct-fired burners. These furnaces can be used for preheating large slabs prior to rolling, or for heating small pre-forged shapes which are loaded in trays or fixtures.
Advantages provided by this type of furnace are continuous processing, and simple mechanics. Disadvantages include high capital cost and large floor space requirement.
Rotary-Hearth Furnace (photo courtesy of Aichelin-Stahl)

Courtesy of Aichelin-Stahl
Rotary hearth furnaces heat the stock on a circular moving bed and are designed for continuous production. The furnace is designed so that the stock is heated to the desired temperature by the time it has rotated into position to be unloaded. Even with the open door for charging and removal, these furnaces are capable of producing modest efficiencies ranging from 15 to 30%.
Advantages provided by this furnace are high speed heating, minimal floor space is needed for continuous heating, and loading and unloading of metal can be accomplished by one operator.
Vacuum Furnace (photo courtesy of the American Gas Association)

Courtesy of American Gas Association
Vacuum furnaces are used to heat material which is sensitive at elevated temperatures to attack by combustion by-products or air. These furnaces are rarely used for heat treating aluminum and are typically only used for high value aerospace products. The material is loaded in the vessel and the vessel is evacuated during heat-up. Vacuum furnaces are typically electrically heated enclosed vessels. Gas fired vacuum furnaces use either shell fired burners or radiant tubes.
